Water>Water framework directive [WFD]>River Basin Management Plan 2009
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Groups
Years
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
-
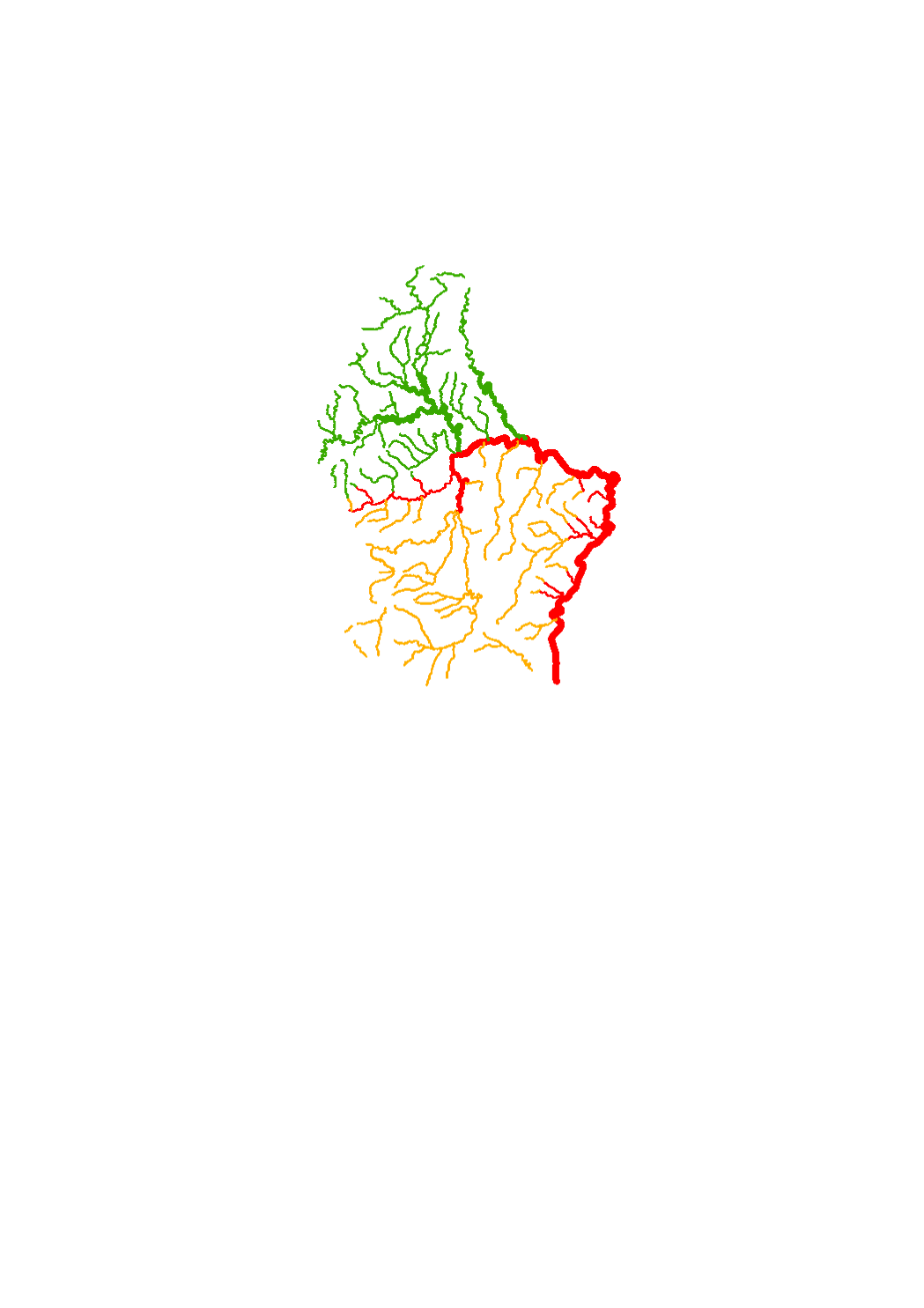
Surface water courses that are part of the monitoring network.
-
A groundwater body is a distinctive volume of groundwater inside one or more aquifers. The identification of a groundwater body is made by geological criteria. A groundwater body is a management unit in order to evaluate the environmental objectives (good status) according to article 6 of the national water law of the 19th December 2008.
-
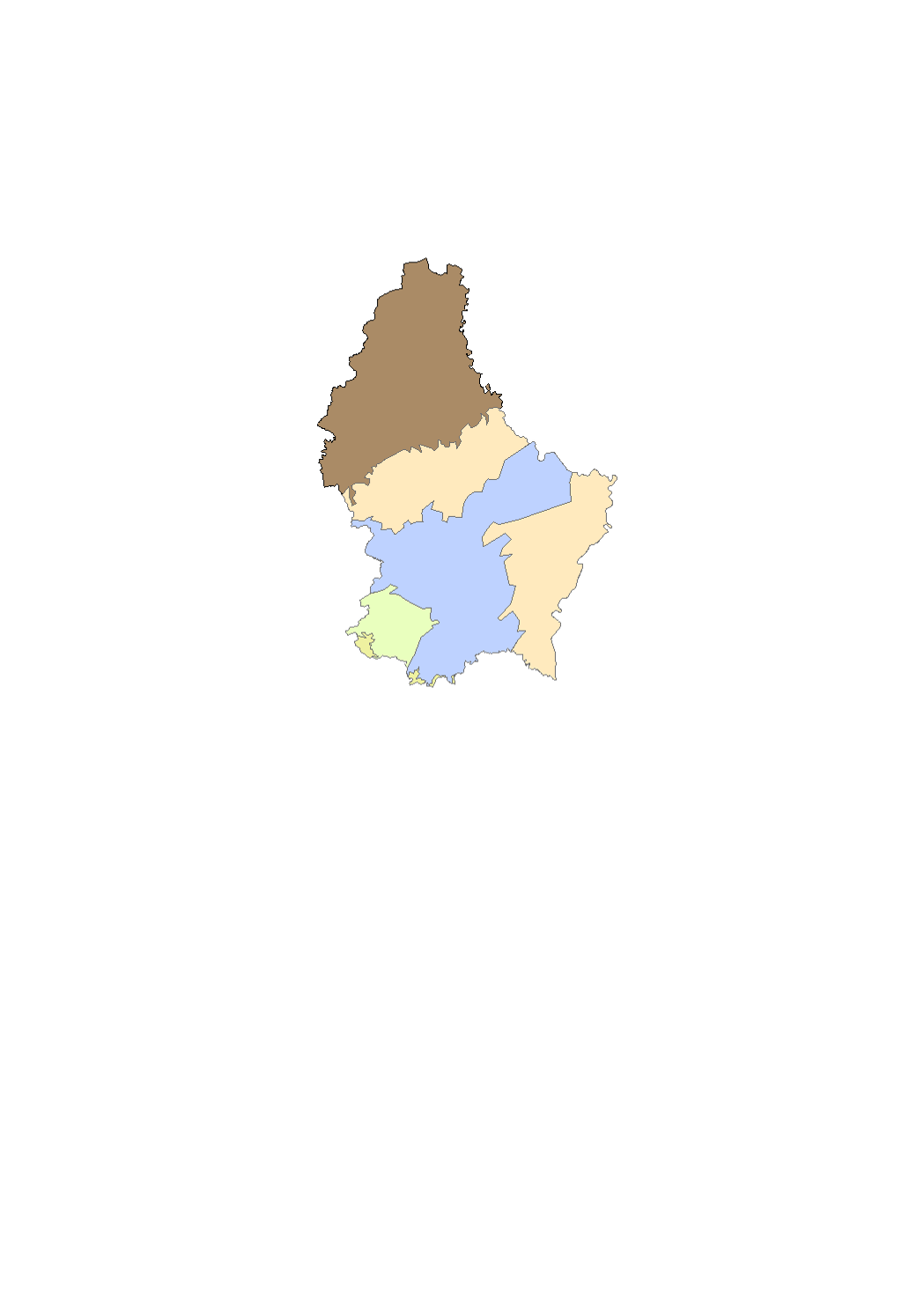
The surface water of Luxembourg are subdivided in 102 water bodies. The identification of water bodies is based on geographical and hydrological determinants. 3 surface water bodies are integrated in the river basin of the "Chiers", part of the river basin district of the Meuse. 99 surface water bodies are integrated in the river basin of the "Moselle", part of the river basin district of the Rhine.
-
The evaluation of the hydromorphological structure of surface water is made in two steps: First the method for the surface water development ability is applied. For this method the current structure of the surface water is analyzed for the different surface water sections. Constructing on the section-referred evaluation a total evaluation of the surface water development ability per surface water body takes place.
-
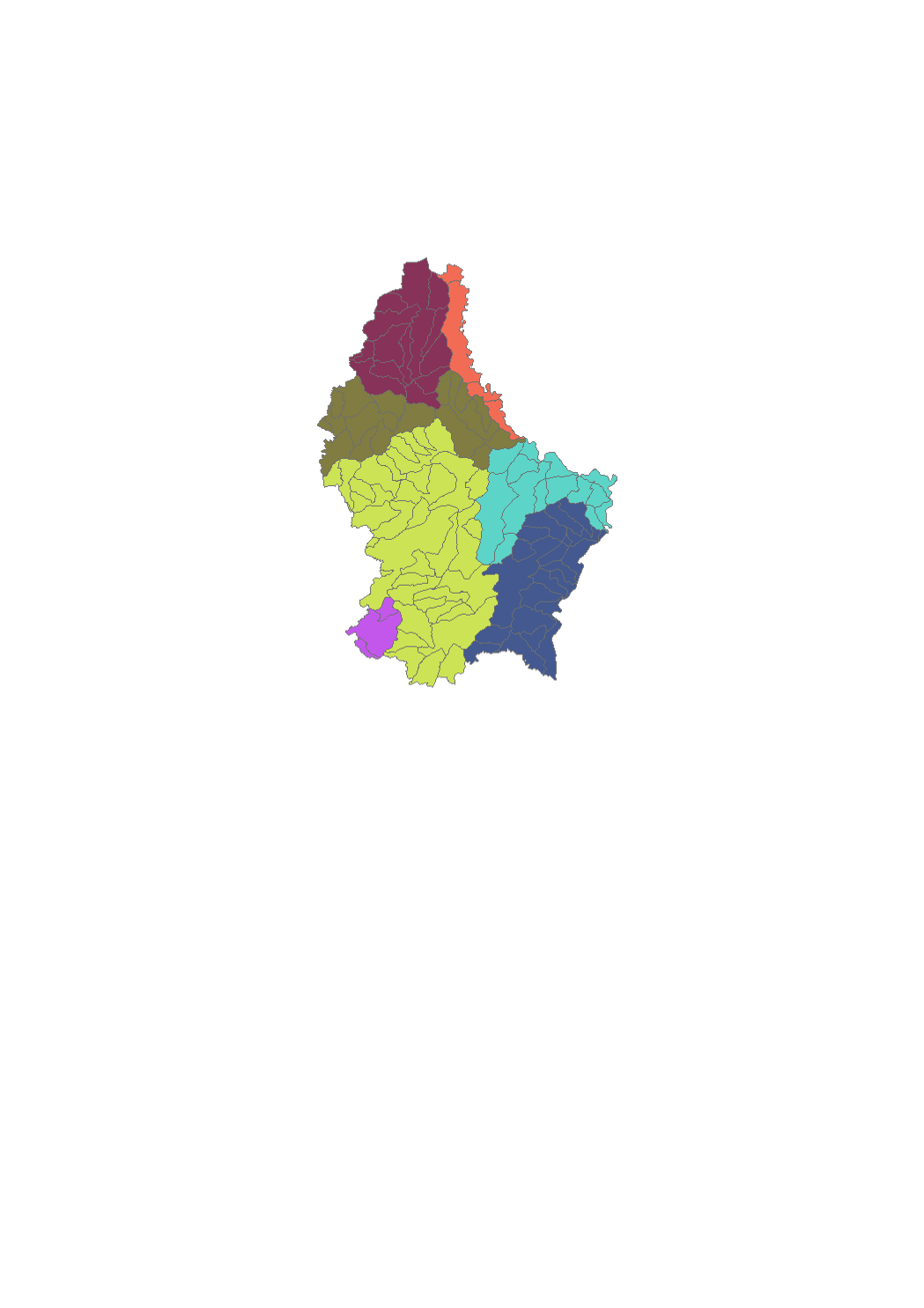
Luxembourg's surface water bodies have been grouped into so-called "study zones", which essentially correspond to the country's major catchment areas. Seven study zones have been designated in total.
-
Representation of the watercourse within a surface water body. Designation of natural surface water bodies and heavily modified water bodies (HMWB). Surface waters which have been physically altered by human activity that they cannot achieve good ecological status as defined by the water framework directive (DIR 2000/60/CE) and that no technical feasibility or cost-effective option exist to stop that human activity, are designated as heavily modified water bodies. These water bodies have the good ecological potential as the environmental objective. They have nevertheless to achieve good chemical status.
-

Representation of heavily modified waterbodies which have been physically altered by human activity that they can not achieve good ecological status as defined by the water framework directive (DIR 2000/60/CE) and that no technical feasibility or cost-effective option exist to stop that human activity. These water bodies have the good ecological potential as the environmental objective. They have nevertheless to achieve good chemical status.
 geocatalogue.geoportail.lu
geocatalogue.geoportail.lu