2021
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Groups
Years
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
-
- Cross-border commuters from the German-speaking community of Belgium to Luxembourg at place of residence (municipalities): 2011-2019 - Territorial entities: municipalities - Commuting data sources: IGSS. Calculations: OIE/IBA 2020 - Geodata sources: NGI-Belgium 2017. Harmonization: SIG-GR / GIS-GR 2020
-
- Cross-border commuters from Saarland to Luxembourg at place of residence (Kreise): 2011-2019 - Territorial entities: Landkreise - Commuting data sources: IGSS 2020. Calculations: OIE/IBA 2020 - Geodata sources: GeoBasis-DE / BKG 2017. Harmonization: SIG-GR / GIS-GR 2020
-
Memorial sites of the Greater Region in 2021 - Sources: Interreg project "Land of Memory", https://www.landofmemory.eu/en
-
- INTER'RED project: Seveso lower tier establishments - Data sources: Partners of the INTERREG V A project INTER'RED
-
Tourist sites illustrated on the tourist map of the Greater Region (2020 edition) - Sources: Interreg project "Digital tourism marketing for the Greater Region", https://tourismus-grossregion.eu
-
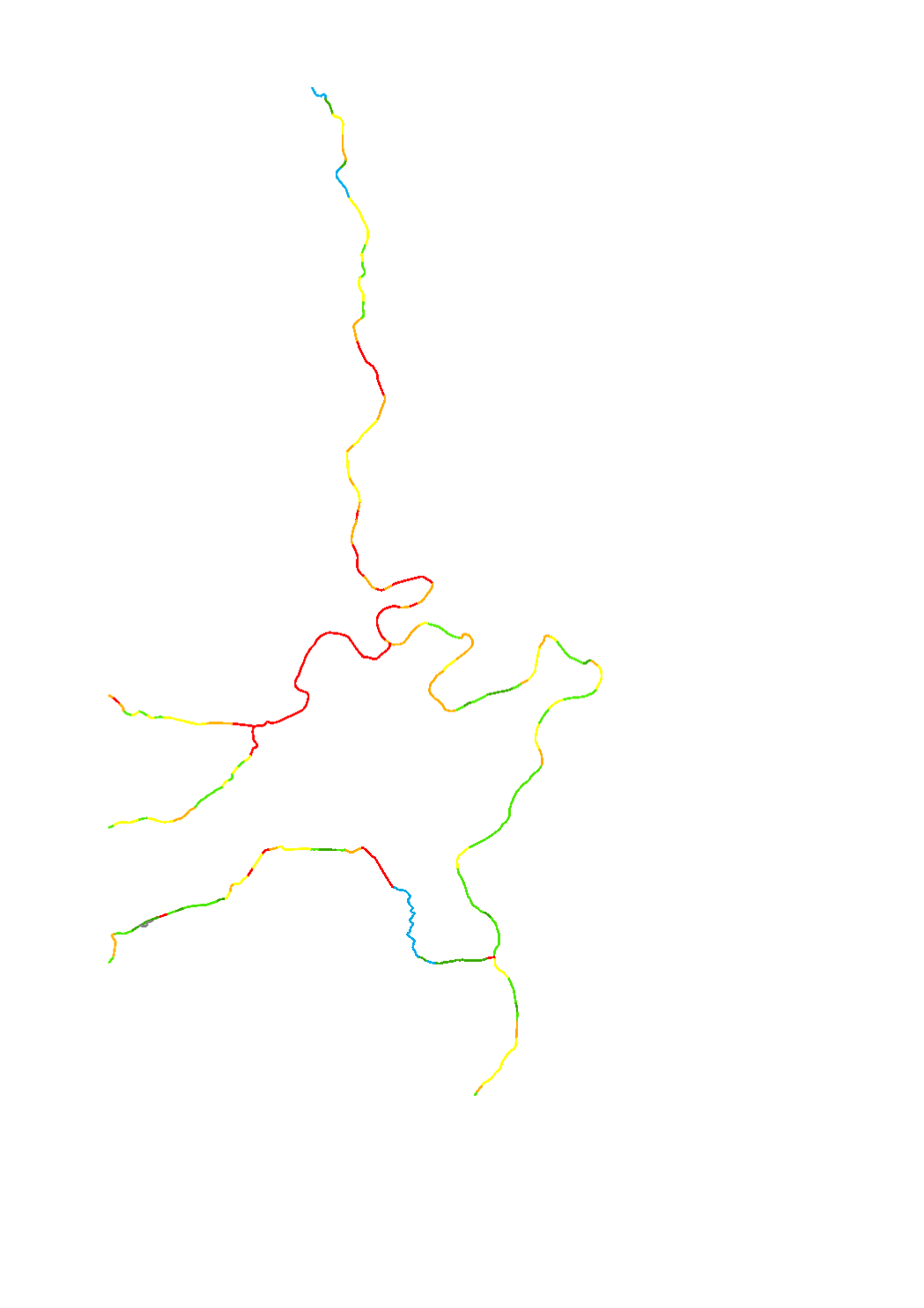
The hydromorphological status was determined by a monitoring compliant with the Water Framework Directive (Directive 2000/60/EU). The elaboration of a structural quality mapping is one part of this monitoring. Within the scope of the work on the structural quality mapping, a total of 31 parameters in the area of the river bed, the river bank and the floodplain are assessed so that the structural quality mapping contains detailed information on the river morphology and the river continuity. In this case, the evaluation of the mapped sections is based on seven classes. The results of the evaluation were aggregated into an overall evaluation per mapped section.
-
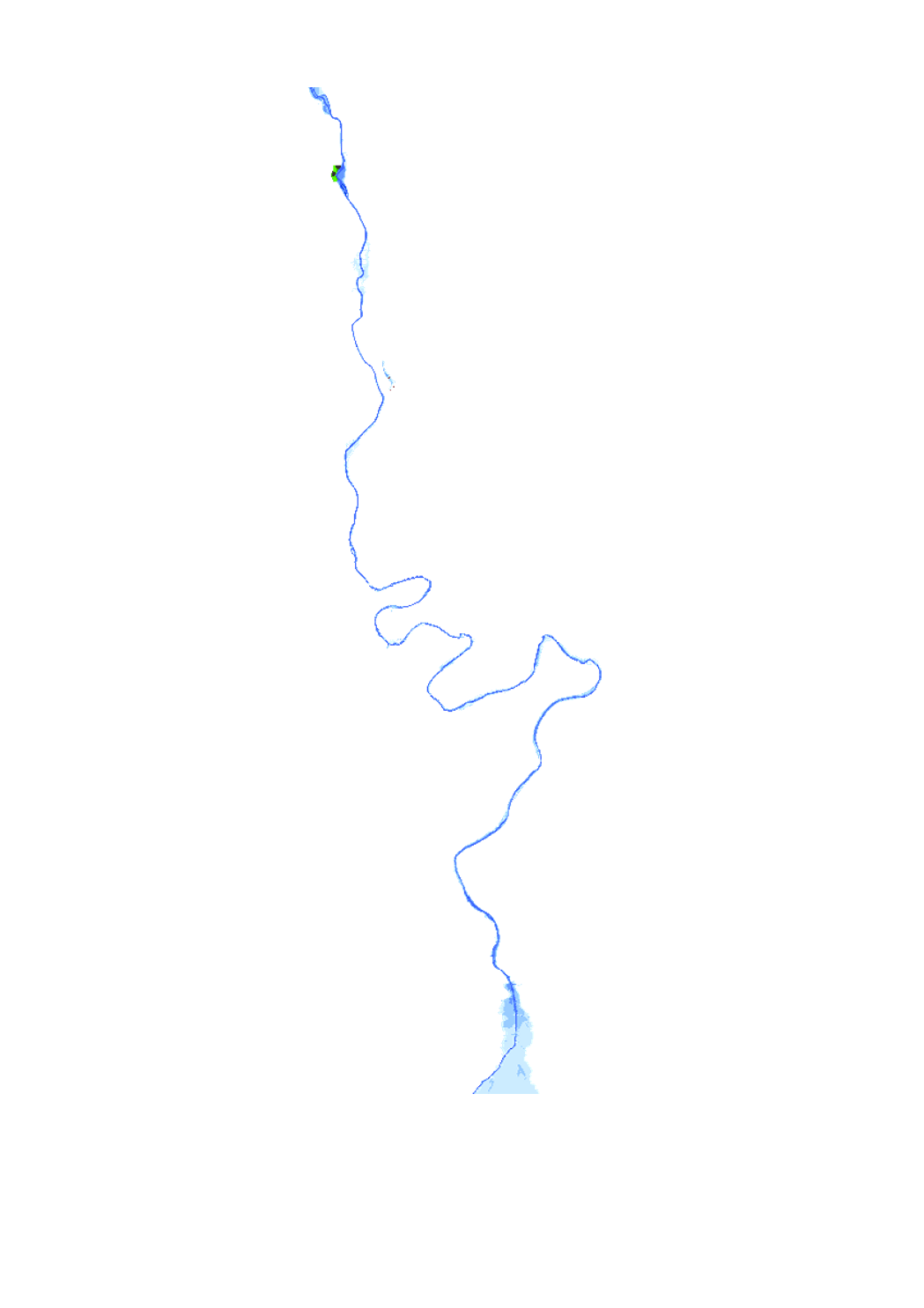
Flood risk map based on the floods directive 2007/60/EC, showing the different affected uses by an 10-year flood event.
-
This layer contains the meteorolgical parameters of the database on agrimeteo.lu
-
This layer contains the meteorolgical parameters of the database on agrimeteo.lu
-

Introduced in 2003 by Directive 2003/87/EC, the greenhouse gas emissions trading system (ETS) is a political instrument in the fight against climate change and an essential tool for reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Industrial operators included in the system according to the rules set by the directive must monitor, declare and have their emissions verified in order to restitute a number of allowances in the EU ETS registry that is equal to their CO2 emissions. To do this, they can receive emission allowances for free, buy allowances or sell allowances.
 geocatalogue.geoportail.lu
geocatalogue.geoportail.lu