Grand Public>Environnement, biologie et géologie>Directive-cadre sur l'eau [DCE]>Plan de gestion 2021>Bewirtschaftungsplang 2021
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Groups
Years
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
-
River protection against the impact of adjacent land use (agricultural runoff such as nutrients and pesticides, fine sediments, cattle trampling, erosion, etc.) through the establishment of fenced riparian buffer stripes, free from any use, where a typical riparian vegetation will grow and provide shade for the river.
-
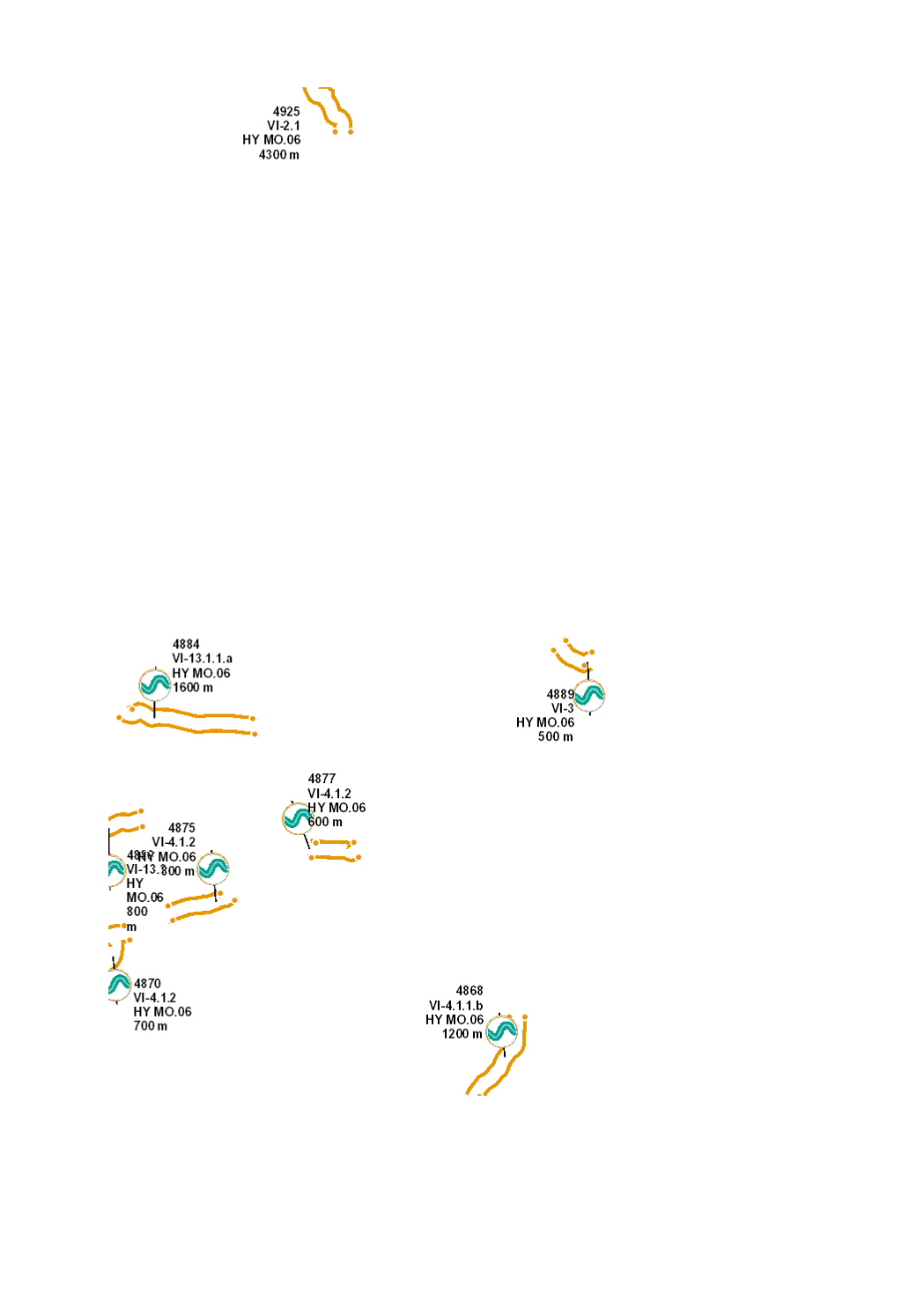
Restoration of the ecological continuity for fish, macroinvertebrates, sediments and terrestrial animals by culverts, through its permanent suppression, or through its adaptation in order to reach natural conditions of substrate, depth, flow rate, luminosity and riverbank structure.
-
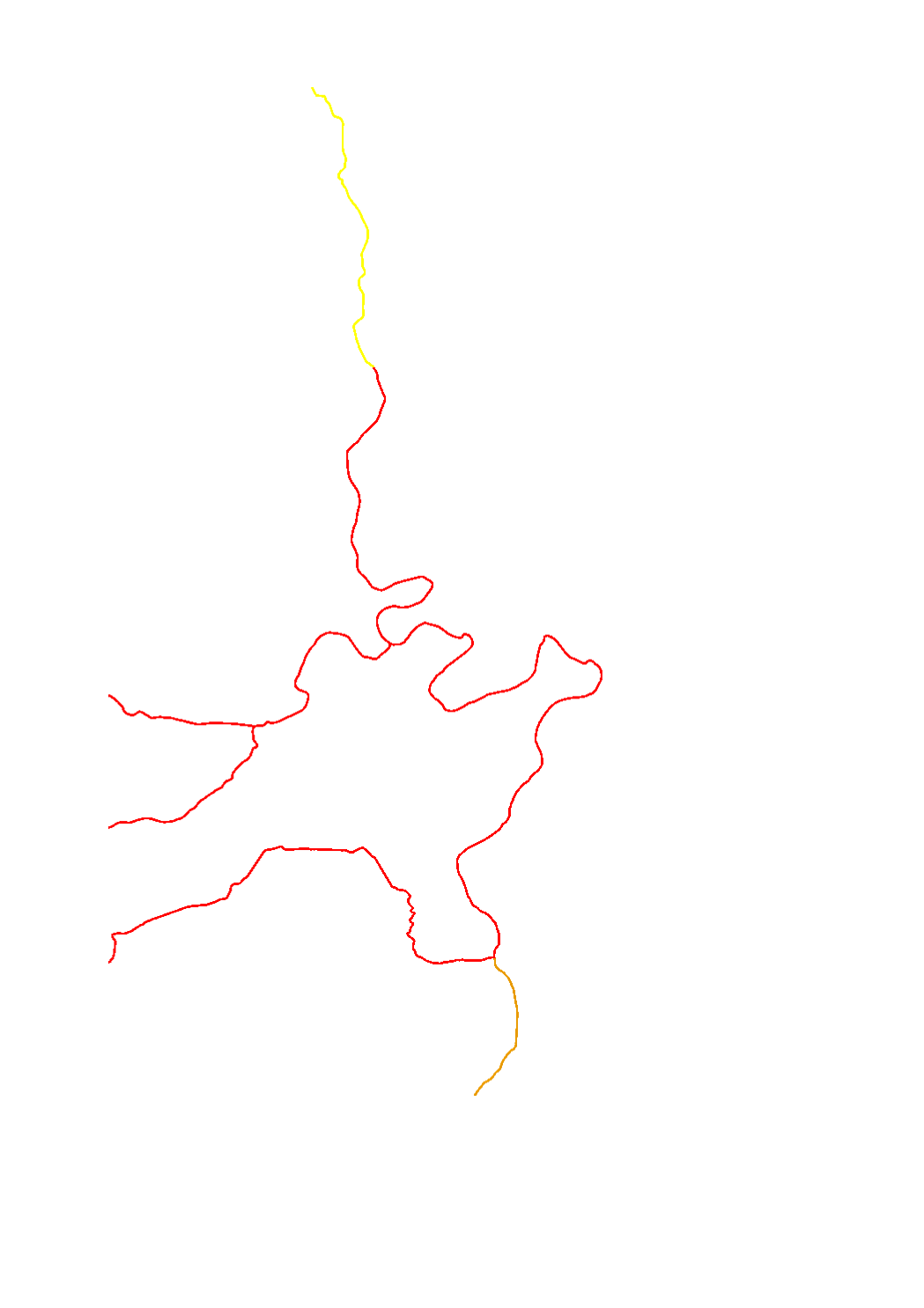
Evaluation of the quality element "hydrological regime" per surface water body
-
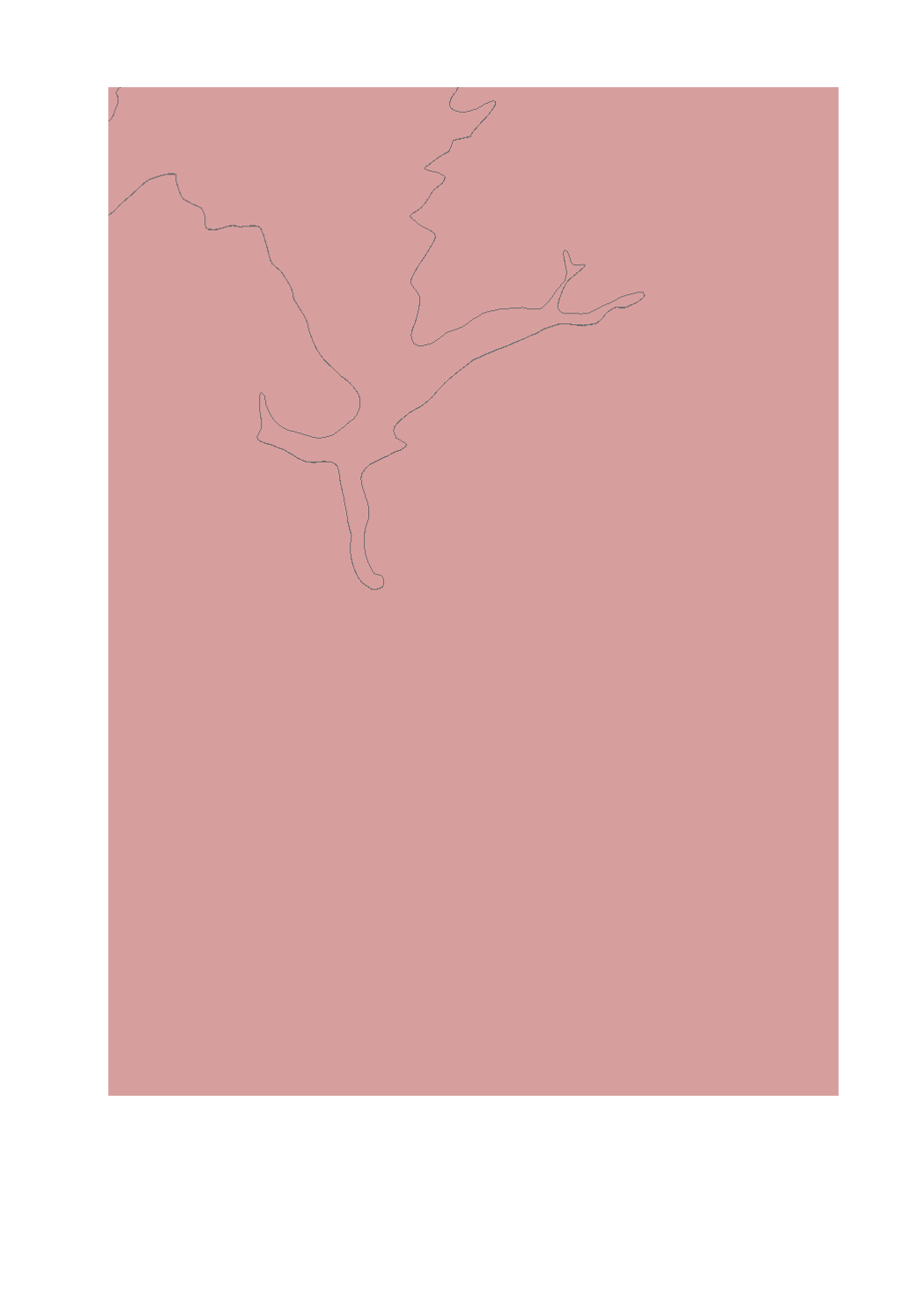

The evaluation of the groundwater bodies is based on the quantitative and the chemical status. The groundwater bodies can be classified as good or as bad.
-
Evaluation of the quality element "continuity" per surface water body
-
Macrophytes are a sub-element of the biological quality element (BQE) of the aquatic flora used for the assessment of the ecological status/potential. The assessment is made in 5 classes : high (blue) - good (green) - moderate (yellow) - poor (orange) - bad (red). Macrophytes are particularly sensitive to organic pollution, trophy and hydromorphology.
-
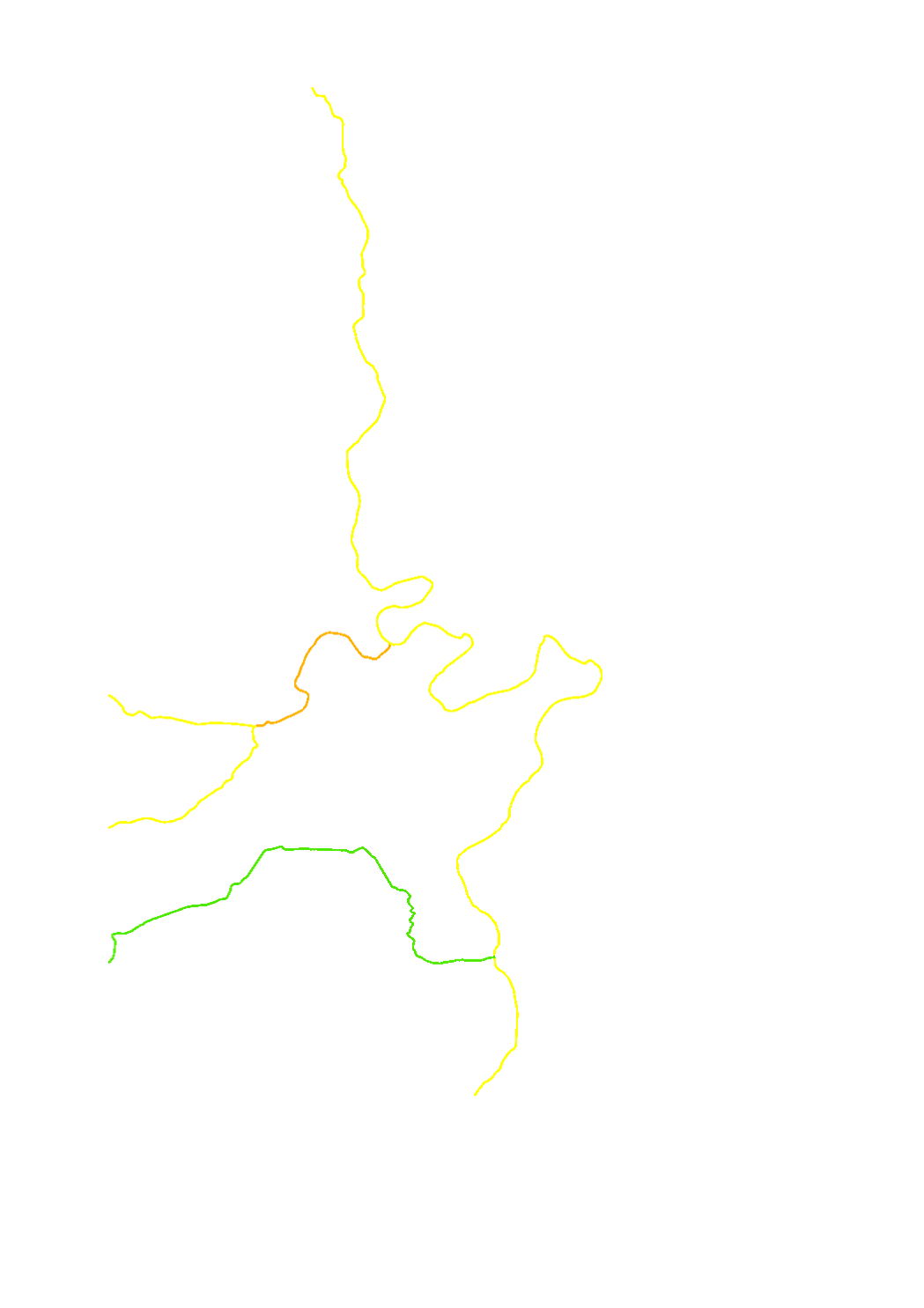
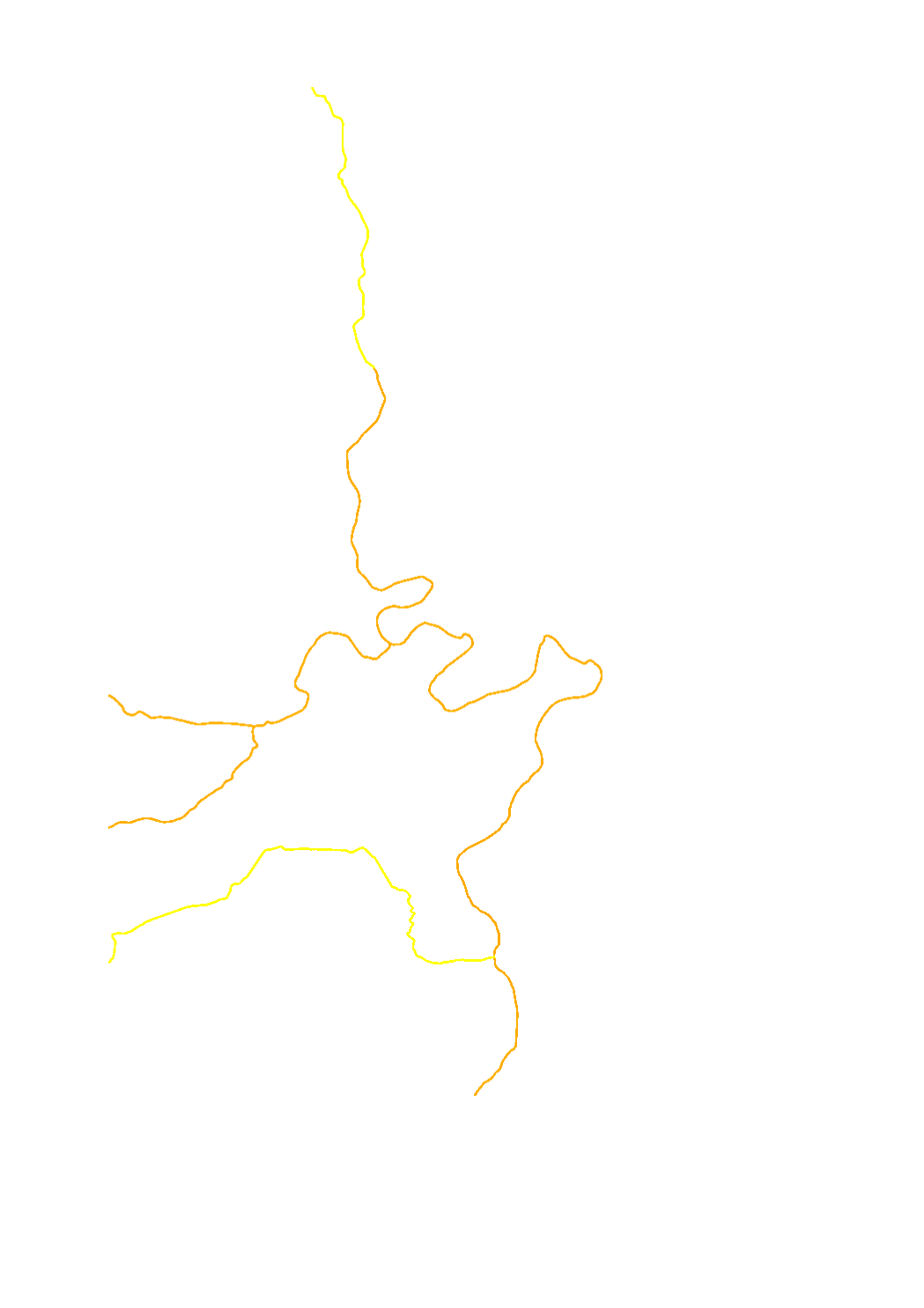
Evaluation of the quality element "morphological conditions" per surface water body
-

The WFD's (2000/60/CE) quantitative status objectives aim to ensure a balance between groundwater withdrawal and recharge.
-
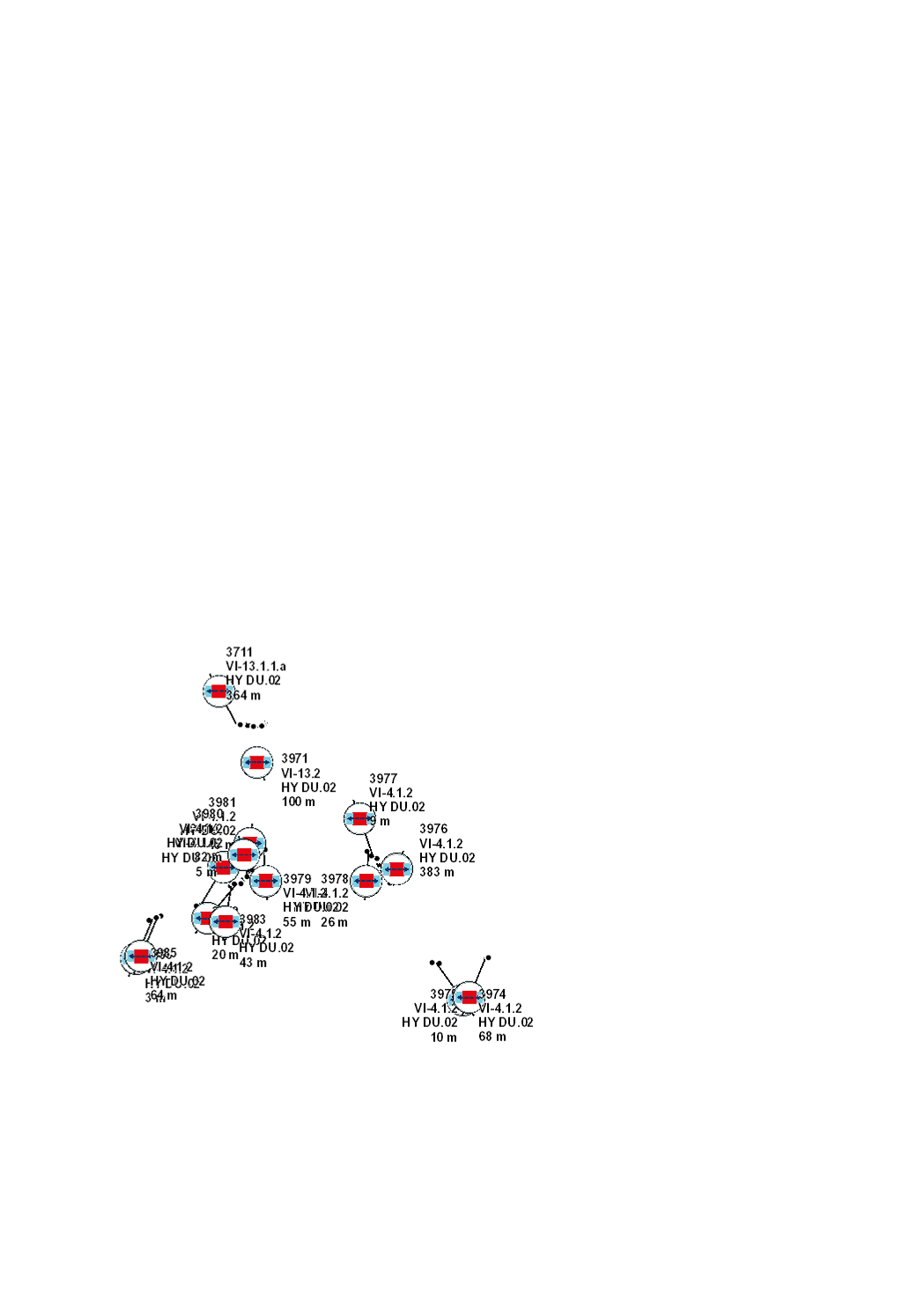
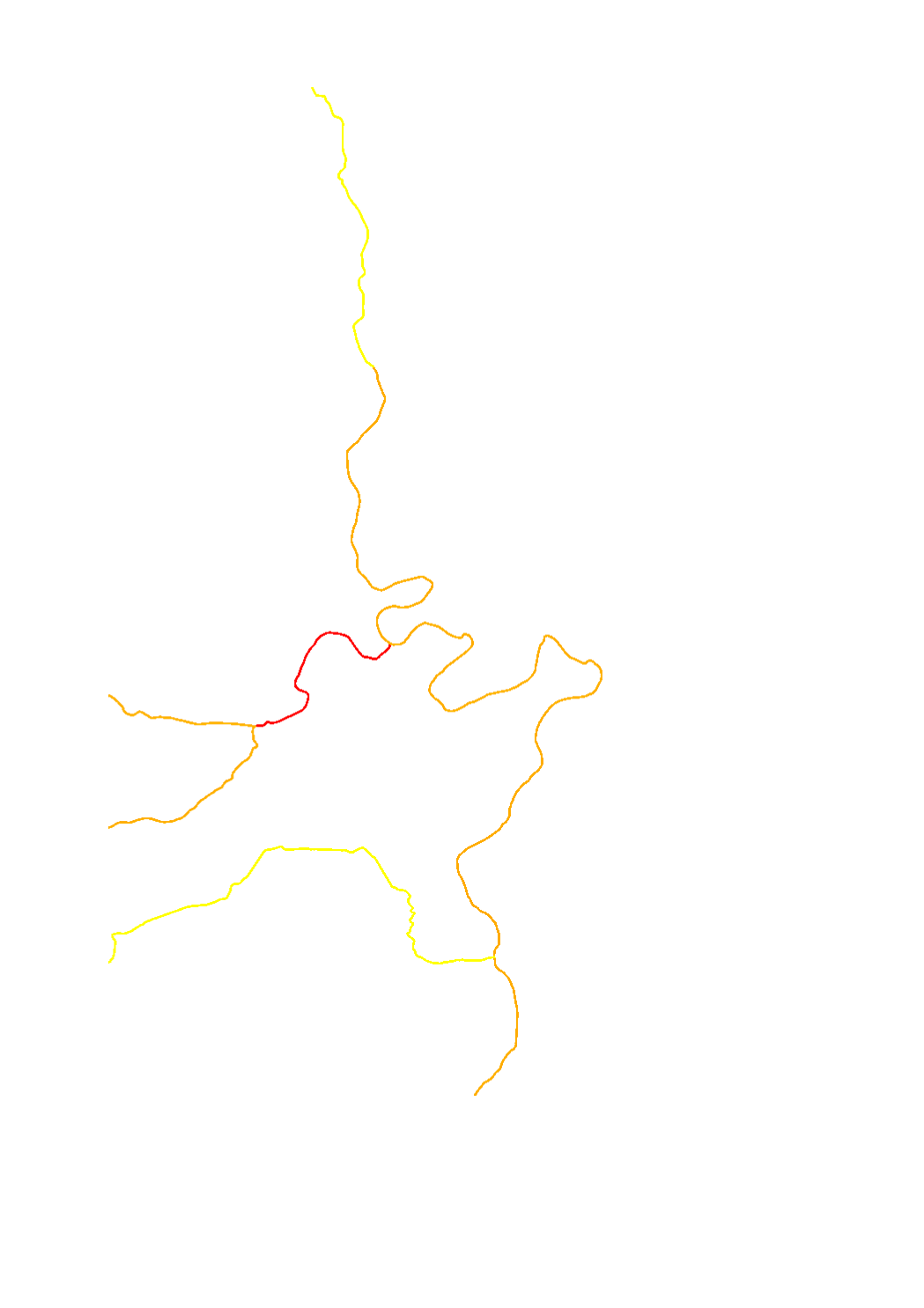
This layer contains the distances to hydrological monitoring stations for which authorisations must first be clarified with the Service Hydrologie (red) or for which the latter must at least be informed (orange and yellow).
-

Monitoring stations for groundwater quality and quantity of the 3rd cycle (2015-2020) regarding the water framework directive (2000/60/CE).
 geocatalogue.geoportail.lu
geocatalogue.geoportail.lu