once
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Groups
Years
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
-
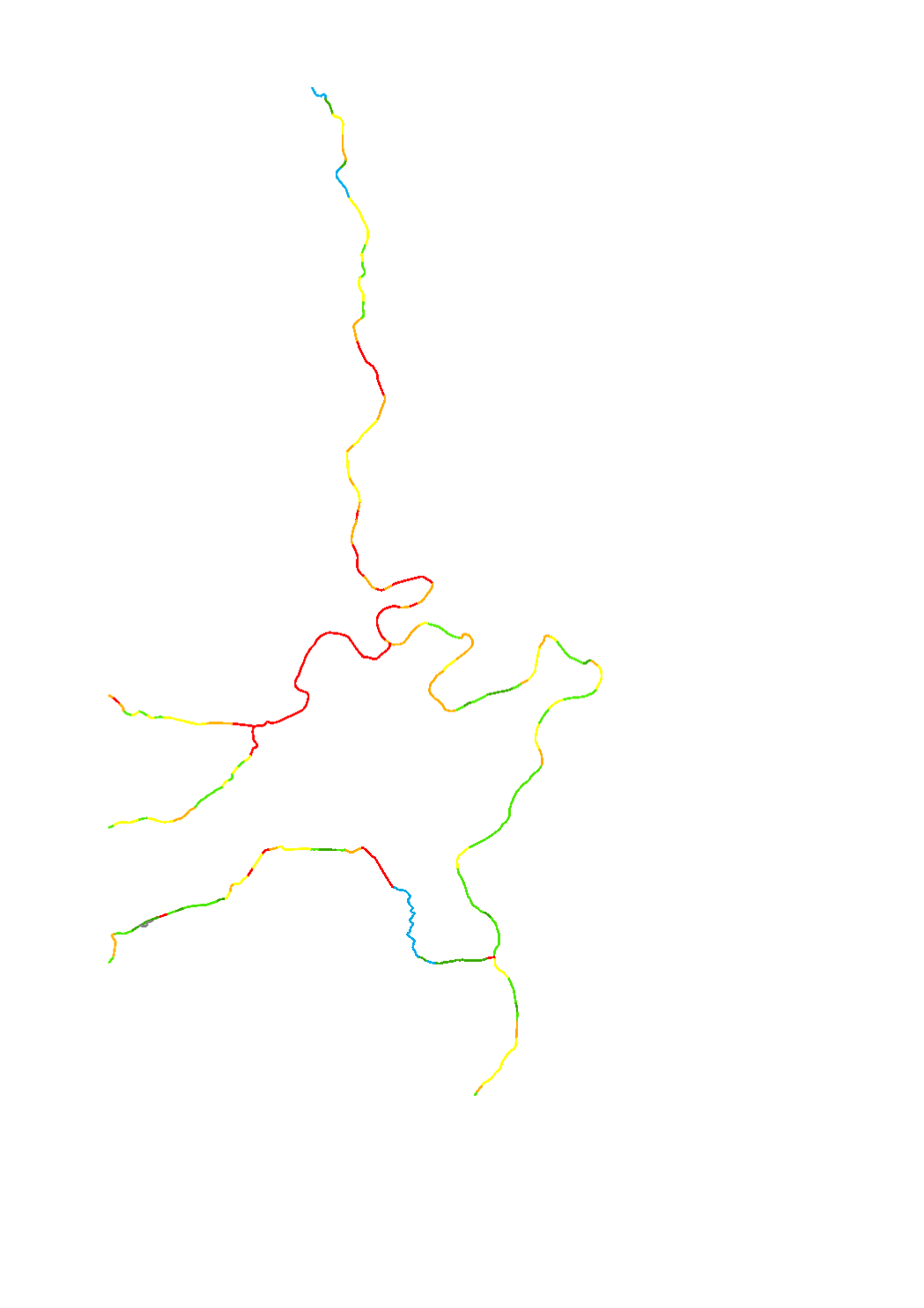
The hydromorphological status was determined by a monitoring compliant with the Water Framework Directive (Directive 2000/60/EU). The elaboration of a structural quality mapping is one part of this monitoring. Within the scope of the work on the structural quality mapping, a total of 31 parameters in the area of the river bed, the river bank and the floodplain are assessed so that the structural quality mapping contains detailed information on the river morphology and the river continuity. In this case, the evaluation of the mapped sections is based on seven classes. The results of the evaluation were aggregated into an overall evaluation per mapped section.
-
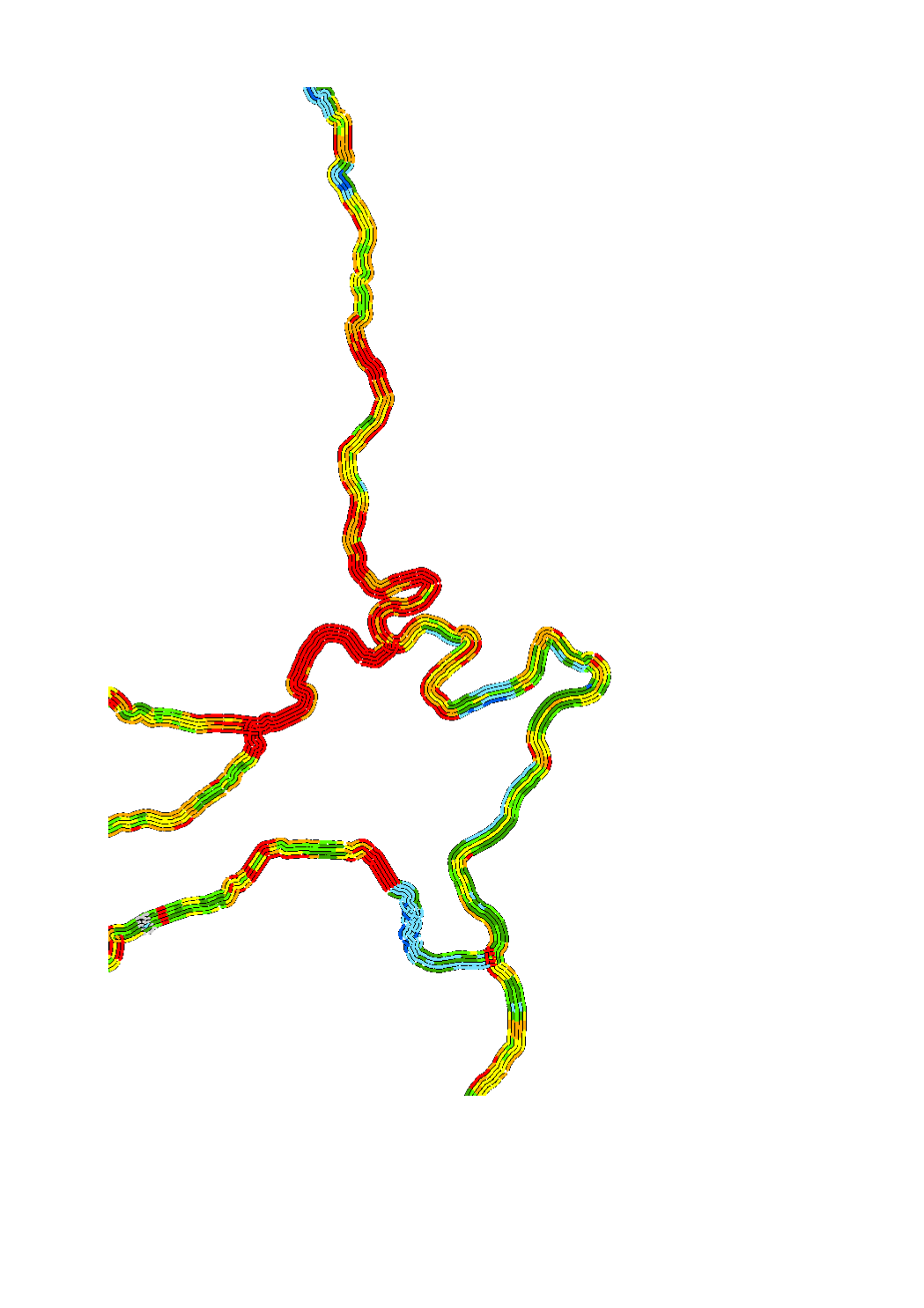
The hydromorphological status was determined by a monitoring compliant with the Water Framework Directive (Directive 2000/60/EU). The elaboration of a structural quality mapping is one part of this monitoring. Within the scope of the work on the structural quality mapping, a total of 31 parameters in the area of the river bed, the river bank and the floodplain are assessed so that the structural quality mapping contains detailed information on the river morphology and the river continuity. In this case, the evaluation of the mapped sections is based on five classes. The areas river bed, left river bank, right riverbank, left floodplain and right floodplain are represented in 5 strips.
-
Cartography of cross profiles of a representative river section every 1000 meters. The assessment of the rate of river incision was calculated from the ratio between bankfull height and bankfull width.
-

Detailed cartography of substrate based on the analysis of 100 meters representative river sections, every 1000 meters.
-
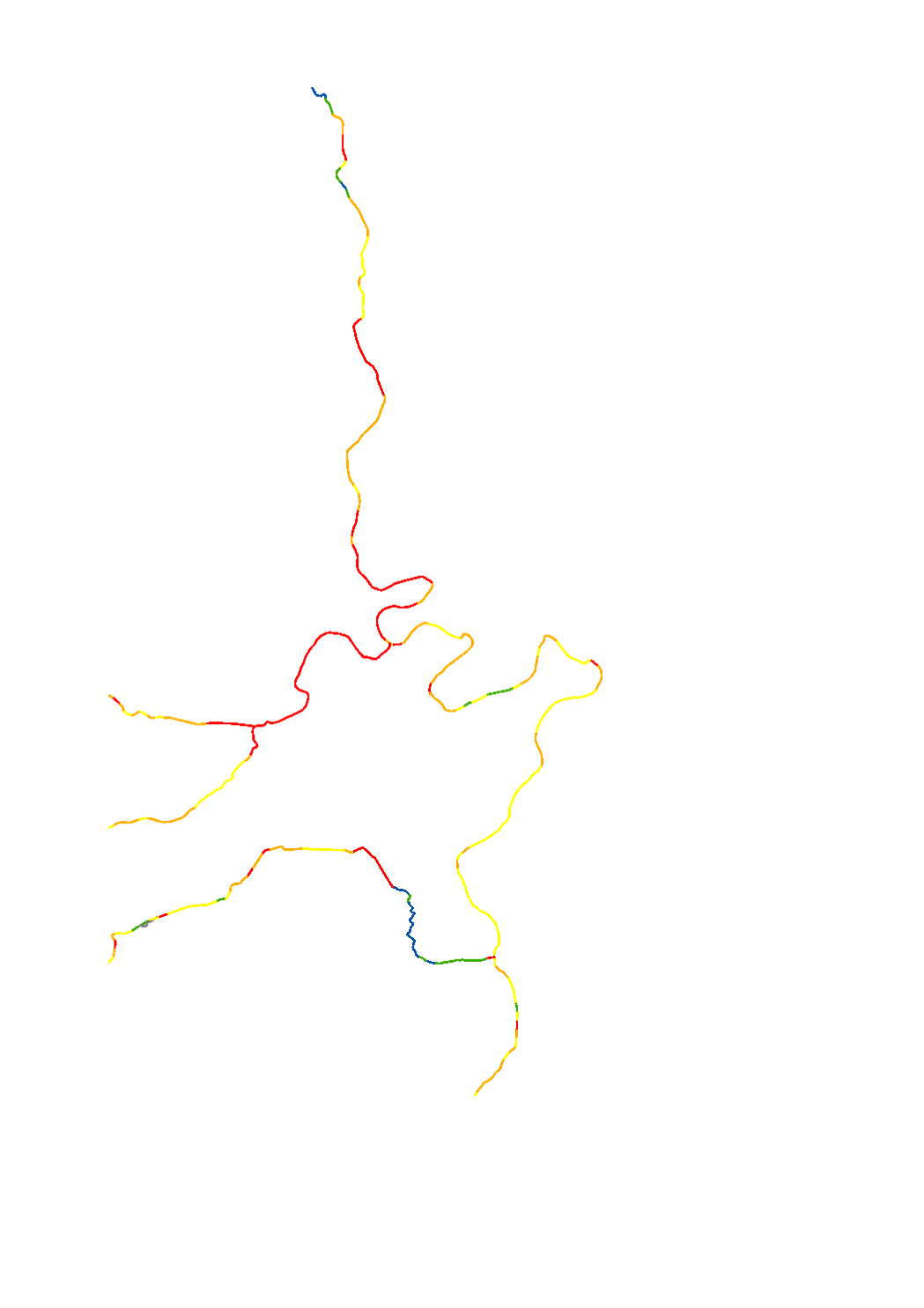
The hydromorphological status was determined by a monitoring compliant with the Water Framework Directive (Directive 2000/60/EU). The elaboration of a structural quality mapping is one part of this monitoring. Within the scope of the work on the structural quality mapping, a total of 31 parameters in the area of the river bed, the river bank and the floodplain are assessed so that the structural quality mapping contains detailed information on the river morphology and the river continuity. In this case, the evaluation of the mapped sections is based on five classes. The results of the evaluation were aggregated into an overall evaluation per mapped section.
-
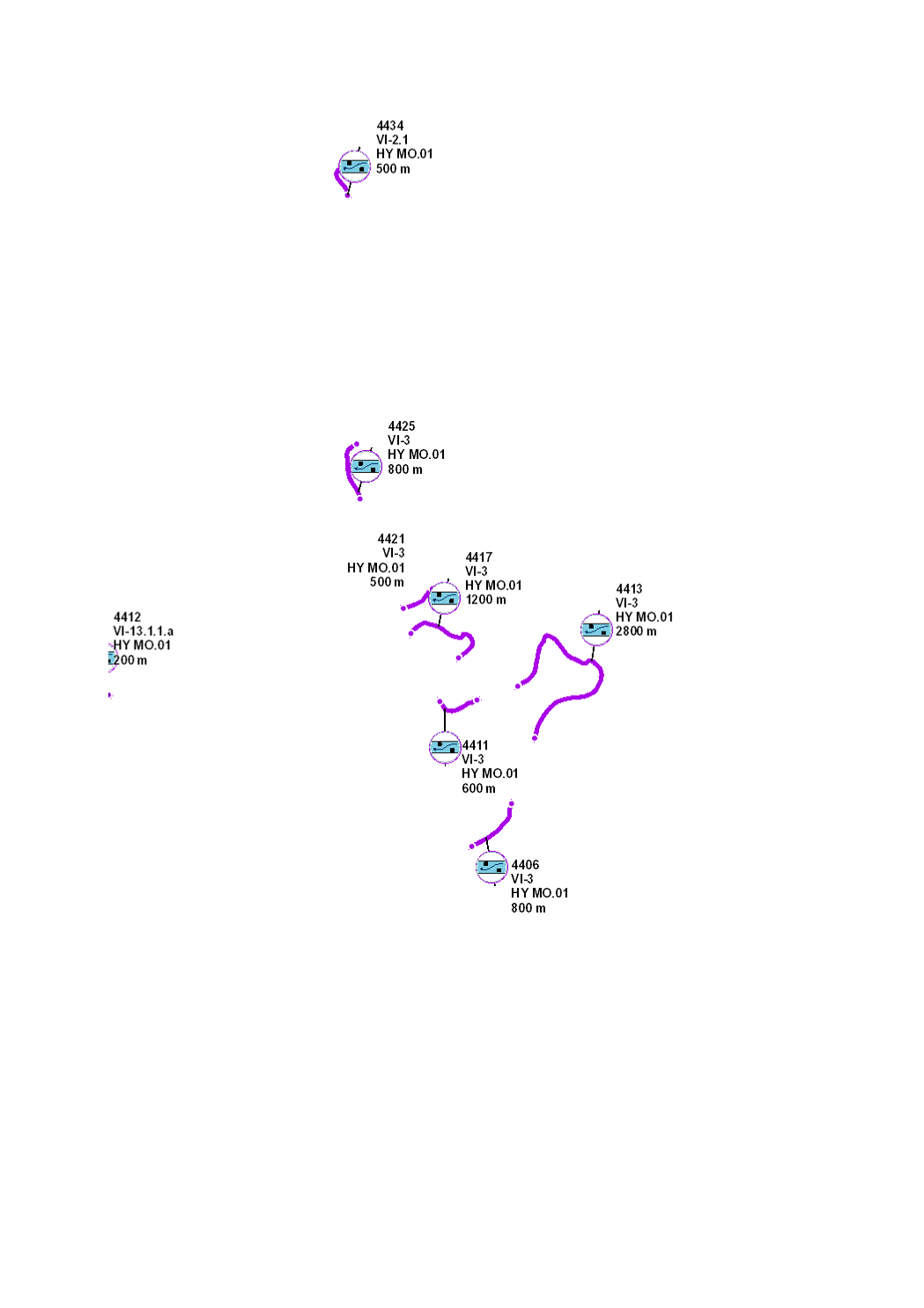
Riverbed diversification through natural substrate supply and/or through the incorporation of structural elements such as stones, rocks, stumps or trunks, in order to recreate a nature-like structure and composition of the bed load, with a low flow channel, a variability of depths and a diversity of flow rates, thus creating microhabitats for the aquatic flora and fauna.
-
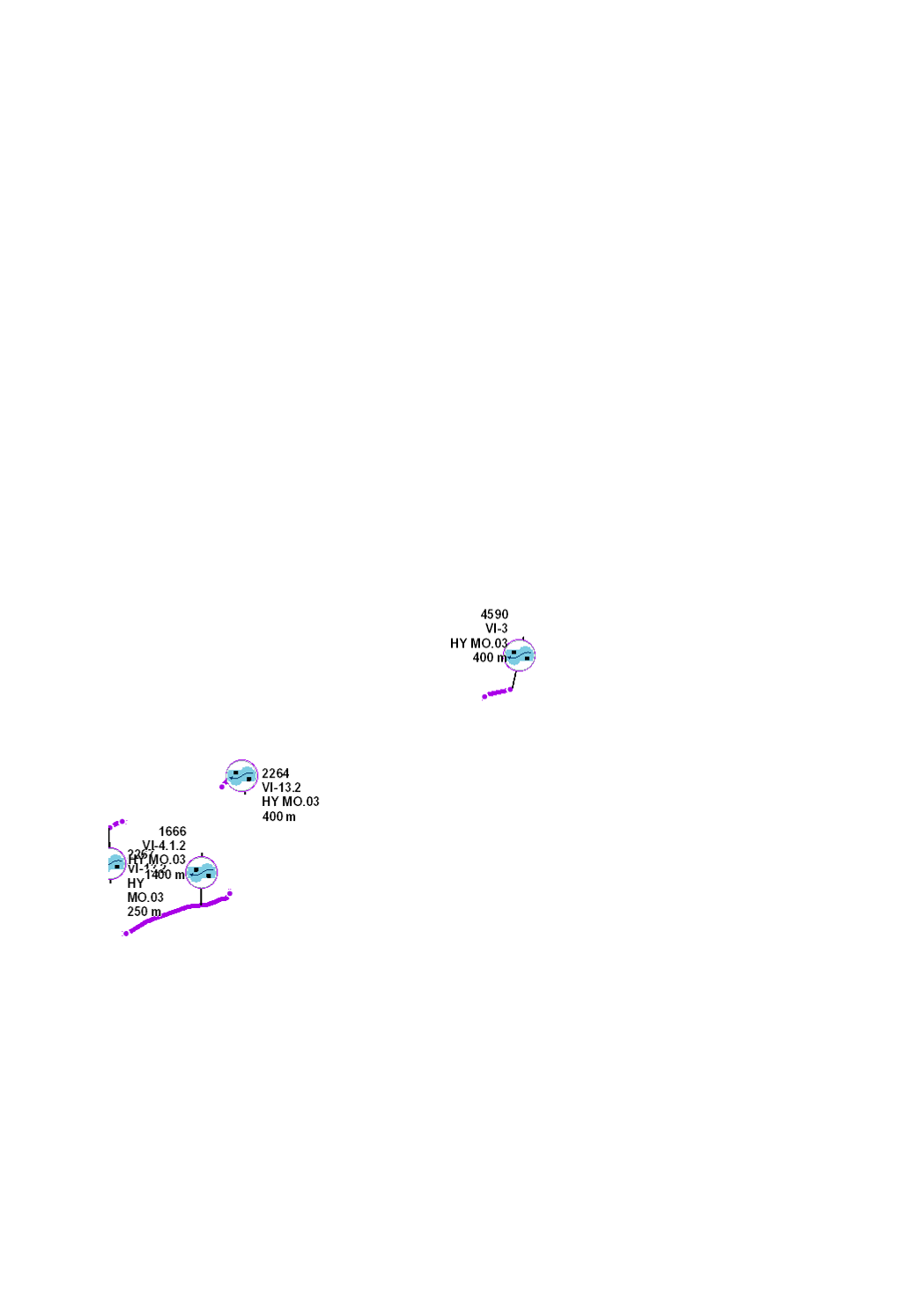
Triggering of river dynamics through placement of flow deflectors such as dead wood or rocks, in order to initiate the formation of diversified structures within the riverbed and the riverbanks (hydrodynamic scour, sedimentation zones, lateral bars, riverbank failure, etc.), creating microhabitats for aquatic flora and fauna.
-
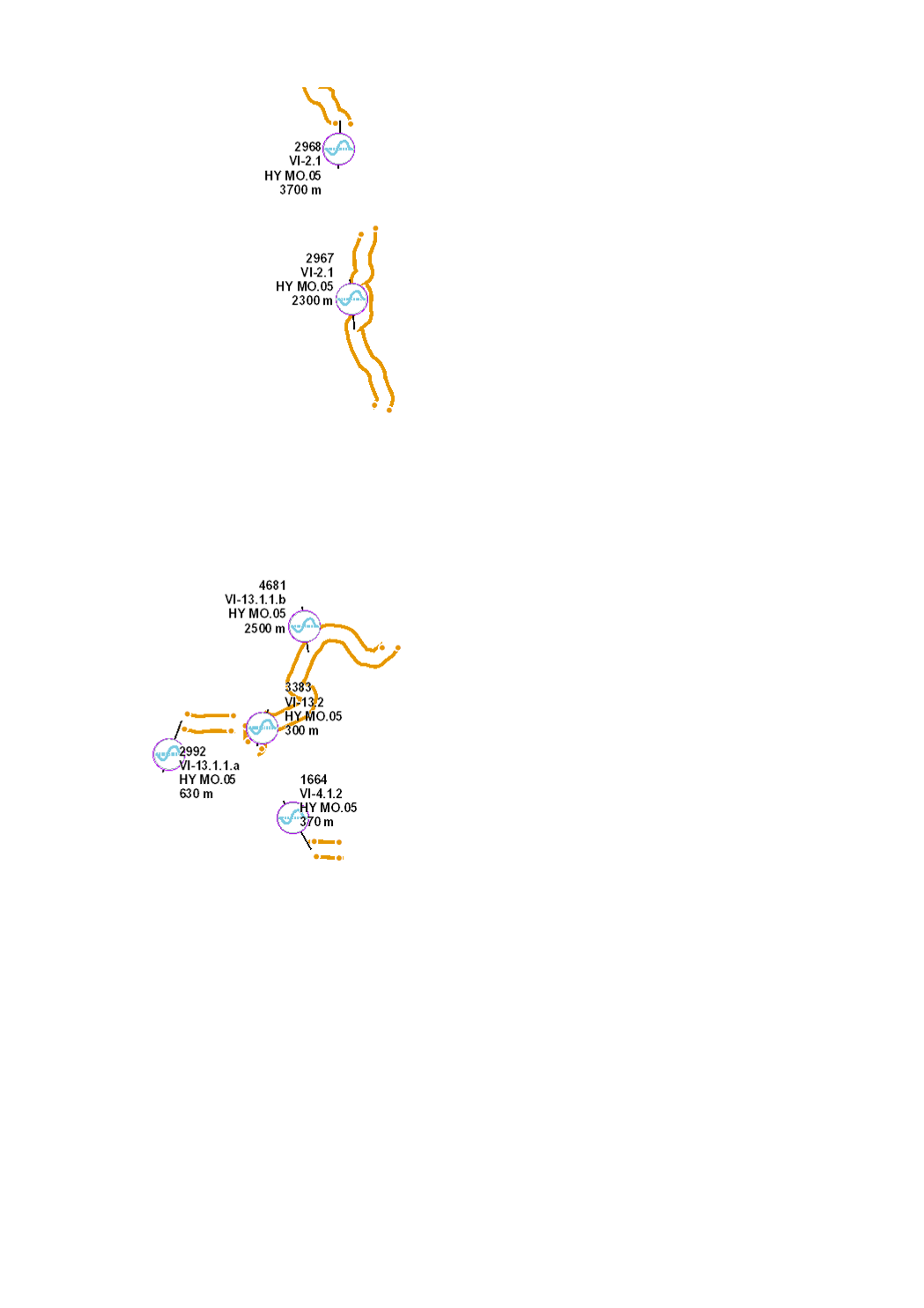
Typical river restoration technique. Re-meandering and restoration of the riverbed in order to recreate a new meandering course compliant with the river typology, with a riverbed and riverbanks rich in structures.
-

Restoration of the connection between the river and its floodplain, oxbow lake reconnection, floodplain extensification regarding land use in order to promote water retention and obtain periodic local inundations downstream. Reactivate a part of the alluvial plain by lowering soil level, thus creating an artificial alluvial plain. Measure promoting aquatic and terrestrial biodiversity of wetlands as well.
-

Restoration of near-natural flow regime at hydropower plants, discharges and diversions. Adapted operation of hydropower plants, verification and, if necessary, restoration of the natural state of discharge points and verification and possible elimination of water abstractions by means of specific studies of alternative solutions and proposals for mitigation measures.
 geocatalogue.geoportail.lu
geocatalogue.geoportail.lu